Can Emergency Care Drain a Boil?
Introduction
Boils are painful and common skin infections that affect people of all ages. These lumps of pus-filled bumps are often a result of bacteria invading the hair follicles or sweat glands. They can appear anywhere on your body but are most commonly found on the face, neck, armpits, and thighs. While most boils heal on their own after some time, there are times when emergency care is necessary to relieve the pain and promote faster healing. In this article, we will look at what boils are, the available treatment options, and how emergency care can help drain a boil if necessary.
Understanding Boils
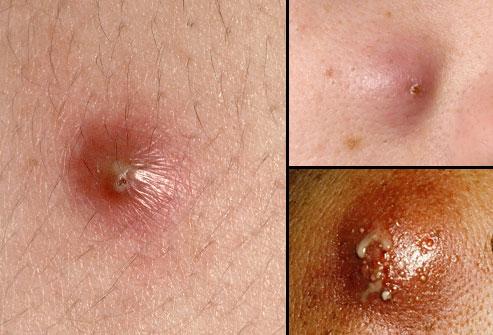
A boil is a type of skin infection that commonly appears on areas of the skin where there is friction or sweat, such as your inner thighs or underarms. They begin as red, tender bumps that slowly grow into hard clusters filled with pus. Some common symptoms of boils include:
- A small red lump that becomes tender and swollen over time
- A cluster of boils forming under the skin
- The skin surrounding the boil becoming inflamed or red
- A white or yellow center filled with pus forms within several days before it ruptures and drains on its own
- Fever in cases where the infection is severe
Boils can be caused by several factors such as poor hygiene, ingrown hair, clogged sweat glands or follicles, weak immune system, diabetes or HIV/AIDS among others. Leaving a boil untreated may lead to further complications like abscesses – a pocket of pus inside the tissue that leaves surrounding tissues vulnerable to bacterial spread.
How to Treat Boils
Boils can be treated using over-the-counter medications, home remedies, or professional medical care. Over-the-counter treatments for boils include antibiotics creams, pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medication.
Antibacterial creams can be applied directly to the boil to destroy the bacteria causing the infection and help speed up the healing process. Pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be taken to ease the pain and discomfort caused by boils. Anti-inflammatory drugs like naproxen or aspirin can help reduce the inflammation and swelling around the boil.
Home remedies can also be effective in treating boils. The most common being a warm compress that involves using a clean cloth soaked in warm water or saline solution, held against the skin over the boil for about 15 minutes several times daily. You can also use tea tree oil, turmeric or garlic which are known for their antibacterial properties, to prevent further infection.
Why Do Boils Need to Be Drained?
Boils need to be drained because they contain pus, which is a mixture of white blood cells, bacteria, and dead skin cells. This accumulation of pus creates tension beneath the skin’s surface causing pain and promoting further bacterial growth in surrounding tissues.
Pus-filled boils need medical attention where they are lanced and drained either by a healthcare provider or self-drainage method after proper guidance from your doctor for appropriate sterile technique ensuring that there is no bacterial spreading complications.
Draining a boil is essential because it helps to expedite healing while also reducing pain and discomfort associated with them. Once relieved from its contents through drainage, it releases some of the pressure on the skin around it, reducing swelling eventually leading to faster healing and preventing abscesses formation if done correctly.
Seeking Emergency Care for a Boil
It is critical to seek emergency care when you have signs that indicate your boil has become infected beyond basic treatment methods. Signs that you may need emergency care for a boil include:
- You have a very high fever – this could be a sign that the boil has progressed into a more severe infection.
- The boil is extremely large and painful
- The boil appears on your face, near your eyes or spine among other regions considered high-risk areas of poor circulation which can lead to complicated bacterial infections.
When you come for emergency treatment, your healthcare provider will evaluate the severity of the situation to note what type of drainage method may be necessary using specialized equipment such as sterile scalpel, syringe or catheter inserted in the affected area.
Emergency care provided by medics is comprehensive when it comes to drains boils as they undergo extensive training in preparation and instrument handling. While using specialized equipment ensures safety measures against infections, some risks remain.
The Risks Involved With Drainage Of A Boil In Emergency Care
There are potential complications associated with drainage procedures that pose an increased risk when done inappropriately or by persons who are not professionals. Here are some of the possible complications one should be aware of before considering having his/her boil drained:
- Bacterial spread
- Sepsis
- Permanent scars
Bacterial spreading is common when the site at which the drain was made gets infected with other bacteria or when bacterial infection isn’t identified and well contained.
Sepsis is a systemic bacterium spread after draining that arises from a wide range of bacteria invading tissues leading to fever and general body malaise.
Invisible scarring could occur due to lancing or unsterilized equipment handling and bacterial contamination by persons without safety awareness and protocols.
There are ways in which complications can be reduced when drainage of a boil is done-consulting a qualified medical practitioner while using safe instruments and sterilized equipment.
Recovery Process After Boil Drainage in Emergency Care
After the boil is drained, it is essential to keep the wound clean and covered to prevent infections that could slow down the healing process. Your healthcare professional may dress the wound or provide you with instructions on how to do so at home.
Additionally, there are several measures you can take to promote quick healing after a boil is drained such as applying antiseptic/anti-inflammatory medications around the area, practicing good hygiene (washing your hands and avoid touching the affected area), keeping the area dry and eating healthy foods that enhance recovery.
Prevention of Boils in Future
While some causes of boils like weak immune system cannot be entirely prevented, other causes can be avoided by adhering to preventive measures like maintaining cleanliness both personally or within your environment, using antibacterial soap and lotions to eliminate bacteria more effectively, good dietary habits and physical activities that promote health.
What To Do If Symptoms Persist
If symptoms persist despite treatment, it’s best to book a follow-up appointment with your healthcare provider for further evaluation. They may prescribe antibiotics to prevent further infections or extended drainage sessions. In severe cases, steroid medication may also be required to aid fast recovery.
Final Thoughts
Boils can cause discomforts and even lead to severe infections when left untreated. It’s essential always to practice adequate hygiene and seek treatment immediately whenever signs show infection has progressed beyond basic treatments. In emergency care, lancing procedures necessitate more professionalism for effective drainage ensuring safe measures against complications’s potential risks like bacterial spreading or scarring. By doing this early enough promotes faster healing, limits pain associated with boils while reducing the risk of serious complications like abscess or bacterial infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Emergency Care Help with a Boil?
Yes, if the boil is particularly painful or large, emergency care can help with immediate relief and drainage. Emergency care may also be necessary if the boil is located in a delicate area that could lead to infection or damage if not properly treated.
What Does the Process of Draining a Boil Involve?
To drain a boil, a medical professional will typically apply warm compresses to the affected area to encourage the boil to come to a head. Then, they will make an incision into the boil to allow it to drain. Finally, they will bandage the wound and provide appropriate aftercare instructions.
Are There Any Risks Associated with Draining Boils?
As with any type of medical procedure, there are risks associated with draining boils. One potential risk of draining boils is infection, as bacteria from the abscess can spread during the procedure. In addition, there may be scarring or skin discoloration in the area where the boil was drained.
What Can Be Done to Prevent Boils from Occurring?
To prevent boils from occurring, it’s important to maintain good hygiene practices, especially when dealing with minor wounds or abrasions. Additionally, having regular skin checks and treating infections promptly can help prevent boils from developing. In some cases, antibiotics may also be prescribed as a preventative measure for individuals who are particularly prone to developing boils.