Understanding the Clear Liquid Discharge from Boils: Causes, Treatment and Prevention
Boils are a type of skin abscess that can cause pain, discomfort, and even fever. A boil is a result of infection that affects one or more hair follicles or oil glands on the skin. When it forms, you may feel a lump beneath the skin, which over time becomes tender and red until it grows to about the size of a pea. The top of the lump then turns white as pus builds up underneath.
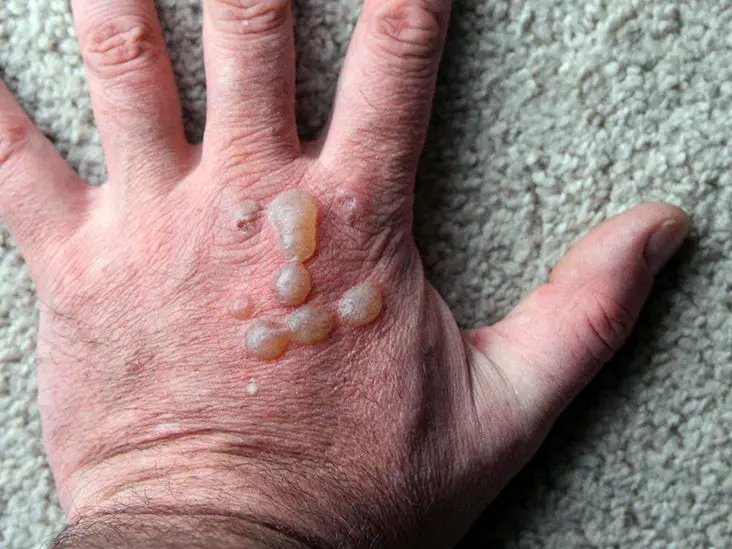
During the healing process of a boil, a clear liquid often oozes out of it. Sometimes you may mistake it for pus-like discharge but it’s important to know the difference as the treatment for clear liquid is different from that for pus-like discharge.
In this article we will discuss what the clear liquid is, why it occurs, and how to treat it. We will also explore prevention strategies and potential complications if left untreated.
What is the Clear Liquid that Comes Out of a Boil?
When a boil has matured and become filled with pus or clear fluid, it usually empties by bursting. This is where the body is attempting to flush out the infected material from inside. However, if there isn’t enough pressure trapped inside to cause bursting or drainage, the boil could heal on its own.
If a boil opens and drains on its own, you’ll probably see this clear fluid mixed with blood still seeping out from within – don’t be alarmed as this can be natural. Clear fluid coming out of boils is common during its healing process and is often referred to as serous discharge.
The fluid is made up of serum produced by your body in response to inflammation. Serum is similar in composition to blood plasma without any clotting factors or blood cells. It appears primarily during early stages when an opening has formed but before the pus begins to come out. Serous fluid contains proteins such as fibrinogen that help to clot the blood, white blood cells, water, and dissolved electrolytes like sodium and potassium.
The amount of clear liquid that comes out of a boil depends on various factors including the size of the boil and the intensity of your body’s inflammatory reaction. It is different from pus which is thick, yellow or green in color and has dead white blood cells and bacteria.
Why Does the Clear Liquid Come Out of a Boil?
Clear fluid discharge from boils is part of the body’s natural healing process. As noted earlier, the fluid consists primarily of serum produced by your body in response to inflammation to help transport nutrients to where they are needed most.
The inflammatory response leads to dilated blood vessels, allowing more serum to enter the affected area, increasing swelling and reducing pain. White blood cells present in serous fluid also work to fight off infections caused by bacteria and other microorganisms.
Boils are typically caused by bacteria named Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus). When S. aureus enters the skin through cuts or cracks, it colonizes hair follicles or oil glands and causes an infection that leads to the formation of a boil. Your body responds by initiating an immune response involving inflammation around the infected hair follicles or sebaceous glands that trigger serous fluid production.
Another possible reason why clear liquid comes out of boils is abscess drainage. An abscess is a pocket of pus within tissue. Sometimes this pus will drain on its own but it can also be removed by surgical incisions if necessary.
How to Treat and Manage Clear Liquid Discharge
While clear liquid discharge during the healing process of boils may be normal, you should still take steps to promote healing and prevent further infection or complications.
The following steps can help you manage discharge:
Cleaning and Dressing: It is essential to keep the area clean and dry to prevent further infection. After cleansing with soap and water, apply a sterile bandage or dressing to cover the affected area. This will prevent contamination and promote healing.
Pain Management: If the boil is causing significant pain, over-the-counter pain-relieving medications such as ibuprofen (Advil) can help manage it.
Antibiotics: If the infection is severe enough, antibiotics may be prescribed by your doctor to treat it and prevent it from spreading to other areas of your body.
Diagnosis and When to Seek Medical Attention
If you are experiencing symptoms like fever, skin redness, swelling, or extreme pain around the boil or if your boil has burst open or produced a lot of pus-like discharge during its healing process, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible. Early diagnosis of boils can help prevent complications that may arise.
A doctor will typically diagnose a boil by examining the lump on the skin surface. If necessary, they may take a sample of the fluid produced by the boil to test for bacteria while ruling out other possible infections.
Boil Prevention
Preventing boils is essential for people with weakened immune systems, those who suffer from chronic illnesses such as HIV/AIDS and diabetes, or those who are more prone to bacterial infections due to their profession.
Some helpful strategies for preventing boils include:
- Maintaining good personal hygiene: Shower daily with soap and water, avoid reusing clothes or towels too frequently, wear clean clothes regularly.
- Avoiding close contact with people who have boils or other contagious skin infections: If you are around someone who has a boil, avoid contact as much as possible until they have fully healed.
- Practice good wound care: If you have a cut or scrape, wash it thoroughly with soap and water, and cover it with a sterile bandage to prevent bacterial infection
- Washing hands frequently: Use soap and water or an alcohol-based sanitizer to wash your hands regularly to prevent the spread of bacteria that might cause boils.
Complications and Long-term Effects
If left untreated, boils can lead to complications like sepsis, cellulitis (an infection in the deeper layers of the skin), or scarring. Those who are at a higher risk of complications include people with weakened immune systems, diabetes, chronic medical conditions, or are on immunosuppressive therapy.
Scarring is another major concern for some people who suffer from boils. Although most boils will heal without leaving any lasting marks on the skin, larger ones may leave behind scars if the tissue damage is significant.
Home Remedies and Alternative Therapies
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure for boils, some home remedies have been passed down through generations that could help relieve symptoms:
- Using tea bags: Applying wet tea bags on the boil could help soothe inflammation because of the antioxidants they contain. This remedy has been used for centuries as an alternative to antibiotics.
- Turmeric: Curcumin is a component of turmeric that has antimicrobial properties. Applying turmeric paste on the boil could help alleviate pain while killing off the bacteria causing the boil.
- Aromatherapy: Essential oils such as tea tree oil have been examined for their antibacterial properties against S. aureus infections due to its Terpinen-4-ol content. Adding it to warm water in a compressor could help alleviate pain and aid in faster healing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about the Clear Fluid from Boils
- What should I do if my boil starts draining fluid? Keep the affected area clean, wash your hands frequently, and avoid contact with others to prevent the spread of bacteria. If there are signs of infection or fever, seek medical attention immediately.
- Will a boil heal faster if I let it drain naturally or should I pop it? Letting it drain naturally is usually best as it’s less risky than popping it which could lead to further infections or scarring. Large boils that do not respond to other treatments may require surgical intervention if they have not drained on their own in several days.
- Can I get boils from poor hygiene? Poor hygiene is not the sole cause of boils, but keeping yourself clean and practicing good hygiene can significantly reduce your chances of developing them.
- Do boils cause permanent scarring? Most boils will heal without leaving lasting scars but sometimes, severe ones can leave behind marks}}
Conclusion
Boils are a common type of skin abscess caused by an infection that affects one or more hair follicles or oil glands on the skin. They’re characterized by redness, swelling, and pain and can be treated with antibiotics and proper wound care. During its healing process, clear liquid discharge is common and is made up of serum produced by your body in response to inflammation. Understanding this discharge is an integral part of promoting healing and preventing further complications.
By following proper hygiene practices, seeking prompt medical attention when symptoms arise, and taking steps to prevent future infections, you can reduce your risk of getting painful boils.
What causes the clear liquid to come out of a boil?
When a boil forms, it is a result of a bacterial infection that results in an accumulation of pus beneath the skin. The clear fluid you see is called serum and is composed of water, electrolytes, and proteins. It is essentially the plasma of your blood without the clotting factors. As a boil progresses, inflammation increases and blood vessels dilate to increase blood flow to the area, causing even more serum to collect.
Is it safe to drain the clear liquid from a boil?
Never try to pop or drain a boil on your own as this can spread the bacteria deeper into the skin or into your bloodstream, leading to further complications. Contact your doctor, who may prescribe antibiotics or may choose to lance and drain the boil in-office.
How long does it take for a boil to heal?
The length of time it takes for a boil to heal depends on its severity. Small boils generally heal within two weeks while larger ones can take up to several months in extreme cases. Additionally, you may require oral antibiotics if the infection has spread, so it’s important not to wait too long before seeking medical attention.
Can I prevent boils from occurring?
Practicing good hygiene can help prevent future boils as they are often caused by staphylococcus bacteria which can be found on the skin’s surface. Cleaning skin with an antibacterial soap and keeping wounds and scratches covered will help decrease your chances of developing another one in the future. If you are prone to boils, it’s also important to maintain a healthy lifestyle with nutritious food and good sleep, as stress and fatigue can weaken your immune system.